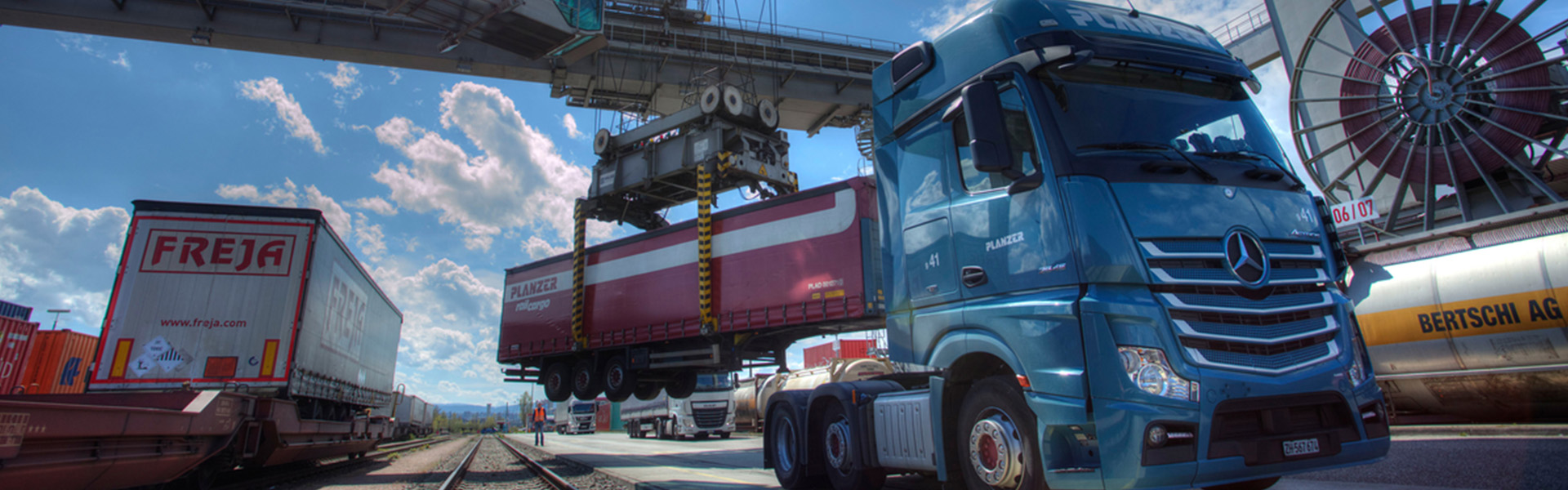
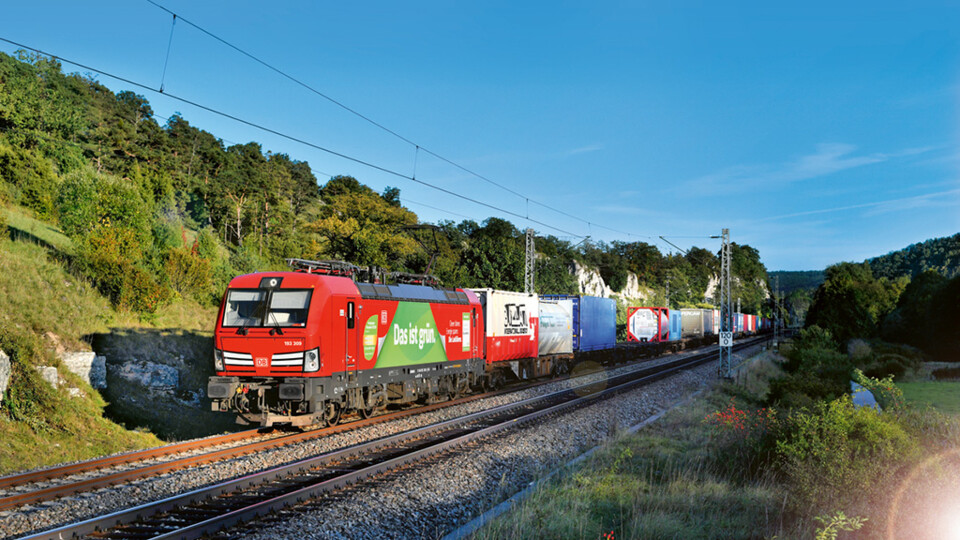
In combined road-rail transport, containers, swap bodies or semi-trailers are transported by rail for the longest part of the journey. It is therefore the transport alternative that guarantees the necessary transport turnaround in these challenging times for climate policy. Freight forwarders and logistics companies benefit from increased road safety, a higher payload and exemptions from taxes and driving bans.
The typical intermodal transport process looks like this: A truck collects goods in a container, swap body or semi-trailer from the consignor. It then takes the load to the nearest terminal so that it can be efficiently transported the longest distance by rail. At the terminal, the freight documents are checked and it is verified whether the loading unit meets the safety requirements for rail transport. A crane lifts the load unit from the truck in the shortest possible time and loads it onto a wagon of the waiting train. The truck is then free again for further transport orders. Once at the destination station, a crane loads the consignment from the train back onto a truck. The truck then transports the consignment directly to the recipient. In addition to the combination of road and rail, the inclusion of the waterway is also a frequently used variant in CT, in which the ship takes over a (further) part of the bundled long-distance transport.

All major industries travel intermodally: automotive, chemicals, mechanical engineering, textiles and food, as well as household appliances and consumer electronics. Car parts and pharmaceuticals, glass and hazardous goods, lettuce and ham, steel and polystyrene cross national borders on the trains. And since hazardous goods also love the railways, Kombiverkehr is a preferred partner for the chemical industry. According to the Federal Statistical Office, rail is 40 times safer than road.
has other advantages as well:

Relieving the road

High transport safety

Securing the supply

Up to four tons more load weight

Exemption from vehicle tax

Toll only in the pre- and post-carriage

Saving of expensive storage capacities

Optimization of the carbon footprint

40 times safer than on the road
There are no longer any limits to intermodal transport, because we offer one of the most extensive CT networks of all. With 162 direct trains per week in German domestic traffic and over 460 trains in international traffic, our network offers maximum flexibility.